Polymorphism in Java
Polymorphism in Java is a concept by which we can perform a single action in different ways. Polymorphism is derived from 2 Greek words: poly and morphs. The word "poly" means many and "morphs" means forms. So polymorphism means many forms.
There are two types of polymorphism in Java: compile-time polymorphism and runtime polymorphism. We can perform polymorphism in java by method overloading and method overriding.
If you overload a static method in Java, it is the example of compile time polymorphism. Here, we will focus on runtime polymorphism in java.
Runtime Polymorphism in Java
Runtime polymorphism or Dynamic Method Dispatch is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than compile-time.
In this process, an overridden method is called through the reference variable of a superclass. The determination of the method to be called is based on the object being referred to by the reference variable.
Let's first understand the upcasting before Runtime Polymorphism.
Upcasting
If the reference variable of Parent class refers to the object of Child class, it is known as upcasting. For example:
For upcasting, we can use the reference variable of class type or an interface type. For Example:
Here, the relationship of B class would be:
B IS-A A B IS-A I B IS-A Object
Since Object is the root class of all classes in Java, so we can write B IS-A Object.
Example of Java Runtime Polymorphism
In this example, we are creating two classes Bike and Splendor. Splendor class extends Bike class and overrides its run() method. We are calling the run method by the reference variable of Parent class. Since it refers to the subclass object and subclass method overrides the Parent class method, the subclass method is invoked at runtime.
Since method invocation is determined by the JVM not compiler, it is known as runtime polymorphism.
Test it Now
Output:
running safely with 60km.
Java Runtime Polymorphism Example: Bank
Consider a scenario where Bank is a class that provides a method to get the rate of interest. However, the rate of interest may differ according to banks. For example, SBI, ICICI, and AXIS banks are providing 8.4%, 7.3%, and 9.7% rate of interest.
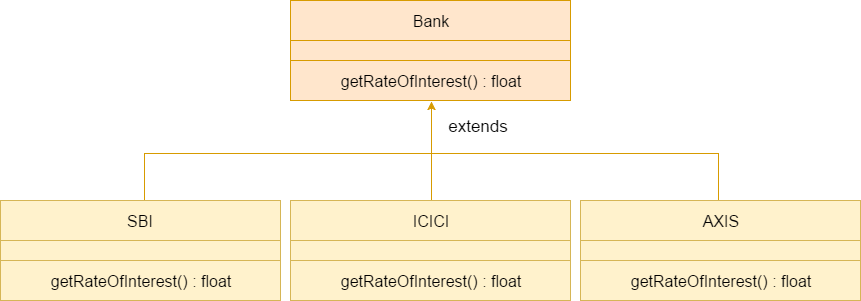
Note: This example is also given in method overriding but there was no upcasting.
Test it Now
Output:
SBI Rate of Interest: 8.4 ICICI Rate of Interest: 7.3 AXIS Rate of Interest: 9.7
Java Runtime Polymorphism Example: Shape
Test it Now
Output:
drawing rectangle... drawing circle... drawing triangle...
Java Runtime Polymorphism Example: Animal
Test it Now
Output:
eating bread... eating rat... eating meat...
Java Runtime Polymorphism with Data Member
A method is overridden, not the data members, so runtime polymorphism can't be achieved by data members.
In the example given below, both the classes have a data member speedlimit. We are accessing the data member by the reference variable of Parent class which refers to the subclass object. Since we are accessing the data member which is not overridden, hence it will access the data member of the Parent class always.
Rule: Runtime polymorphism can't be achieved by data members.
Output:
90
Java Runtime Polymorphism with Multilevel Inheritance
Let's see the simple example of Runtime Polymorphism with multilevel inheritance.
Test it Now
Output:
eating eating fruits drinking Milk
Try for Output
Test it Now
Output:
Dog is eating
Since, BabyDog is not overriding the eat() method, so eat() method of Dog class is invoked.
